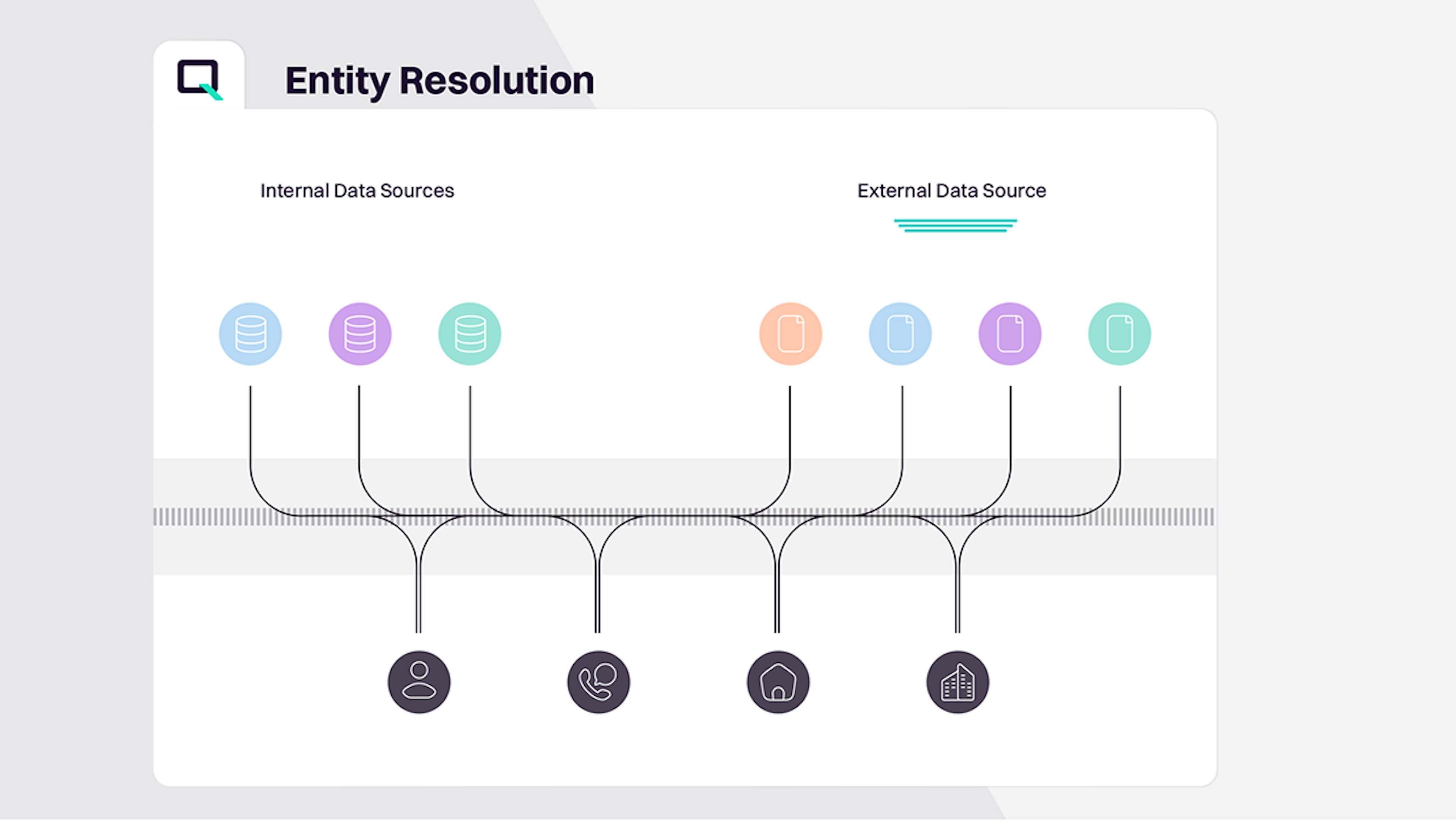
What is data fabric?
Data fabric refers to an architecture and set of data management practices that enable organizations to create a unified and integrated view of their data across various locations and formats.
It uses intelligent metadata-driven data integration to create an enterprise-wide knowledge graph as a service to empower better decision-making and data-driven apps.
Data fabric aims to break down data silos and provide a more holistic and agile approach to data management, supporting modern data-driven businesses. It's particularly relevant in the context of the increasing complexity of data ecosystems, where data is distributed across various platforms, databases, and applications.

Data fabric core capabilities
There are several characteristics to consider when thinking about a Data Fabric architecture like scalability, security, flexibility, real-time data processing and more. The key components include unified data access via an Enterprise knowledge graph, data integration, data orchestration, and metadata management.
Enterprise knowledge graph
Creates a joined-up, unified, and coherent view of enterprise data from existing messy, distributed sources and democratizes access for transactional and analytical use cases to drive better decision making with more complete and accurate data.
Data integration
Automatically and dynamically integrates with existing data sources to bring data together, simplifying the work required to acquire and prepare data for a data driven project.
Data Orchestration
Coordinates and manages data workflows and processes to ensure data movement, transformation, and analysis in a seamless manner.
Metadata management
Automatically catalogues the data available in the enterprise to create a unified model that can be used for designing and managing data throughout its lifecycle whilst ensuring compliance with policy and regulations.
What are the benefits of using data fabric?
Here is an overview of the benefits:
Consistent view of data
By utilizing knowledge graphs, metadata management and ML techniques, data fabric enables a consistent and unified view of data across various sources and locations, making it easier for users to access and analyze information without dealing with data silos.
Data democratization
A data fabric architecture enables simpler creation and reuse of data products, expanding data accessibility beyond technical teams.
Data quality
Data fabric can help maintain and improve data quality by providing mechanisms for data cleansing, validation, and consistency checks across different data sources.
Seamless integration
It facilitates the integration of data from disparate sources, including on-premises systems, cloud services, and various databases, allowing for a more holistic understanding of information.
Adaptability
Data fabric promotes agility by allowing organizations to adapt to changing business needs, technologies, and data sources without major disruptions.
Consistent data governance
Implementing data fabric often involves establishing consistent data governance policies, ensuring that data is managed, protected, and used in compliance with regulatory requirements.
Scalable architecture
Perpetual KYC systems are designed to adapt to changes in regulatory requirements. The ongoing nature of the process allows financial institutions to stay compliant with evolving regulations and guidelines.
Real-time analytics
It enables real-time or near-real-time access to data, allowing organizations to make more informed decisions based on the latest information.
Resource efficiency
Data fabric can contribute to cost savings by optimizing resource usage, reducing redundancies, and improving the efficiency of data management processes.
Enhanced security measures
A well-designed data fabric includes security features that help protect sensitive information, ensuring data privacy and compliance with data protection regulations.
What problems does data fabric solve?
Limited access to data
One prominent issue it addresses is the complexity associated with accessing data. In traditional setups, accessing data can be convoluted, requiring technical expertise and creating bottlenecks.
Inconsistent data across the organization
Data fabric tackles the problem of inconsistent data across applications, providing a unified and cohesive view by seamlessly integrating information from disparate sources.
Inaccurate and incomplete data
It addresses the challenges of accuracy and completeness of data, offering mechanisms for validation and cleansing.
Complicated data landscape
Data fabric simplifies the intricate data landscape by providing a unified framework, making it more navigable and ensuring that businesses can harness the full potential of their data resources.
Data fabric use cases:
Data fabric can be applied to various use cases across different industries, providing organizations with a unified, efficient, and scalable approach to leverage their data assets.
Decision Intelligence
For example, a data fabric architecture can support a Decision Intelligence platform. Decision intelligence involves leveraging data and analytics to make informed and effective business decisions. Data fabric can play a crucial role in decision intelligence by providing a unified and consistent data environment.
Customer Intelligence
Creating a comprehensive and unified view of customer data by connecting data from various touchpoints, enabling businesses to gain insights into customer behavior, preferences, and interactions.
Supply Chain Integrity
Connecting data from various supply chain elements, such as suppliers, manufacturers, and logistics providers, to create a unified view that enhances visibility, coordination, and efficiency in the supply chain.
Financial Crime and Fraud prevention
Detecting and preventing financial crime and fraud by aggregating and analyzing data from multiple sources in real-time, allowing organizations to identify suspicious patterns and take timely action.
These are just a couple of examples of the versatile application of a Data Fabric architecture. By providing a trusted view of an organization’s data, the possibilities are endless across Government, Healthcare, Banking, Insurance, Telecommunications, and more.
Is data fabric the same as data virtualization?
While both data fabric and data virtualization aim to address data integration challenges, data fabric has a broader focus on creating a unified and consistent data environment that can be accessed and shared across the organization. It is an end-to-end data management architecture that aims to eliminate data silos by connecting data from different sources. It is beneficial for addressing challenges related to data complexity, accessibility, and governance.
On the other hand, data virtualization emphasizes providing a virtual layer for seamless access to data without physical movement. It integrates data from disparate sources without physically moving or replicating it. Data virtualization is well-suited for scenarios where real-time access to integrated data is crucial without the need for extensive data movement. It is often used for analytics, reporting, and business intelligence purposes.
The choice between them depends on the specific needs and goals of an organization.
What is data fabric vs mesh?
Both data fabric and data mesh are concepts related to data architecture and management, but they approach the challenges of distributed and diverse data ecosystems in slightly different ways.
A Data Fabric is centrally managed and focuses on integrating and connecting data across the entire organization, reducing data silos, and ensuring a consistent and accessible view of data for users. It is better for leveraging data from existing systems to enable incremental and co-existent transformation to a unified view of enterprise data.
Data mesh emphasizes decentralized data ownership and architecture, aiming to treat data as a product and applying principles of domain-oriented decentralized data architecture. Data Mesh is better for greenfield architectures or where significant technology and organizational transformative change is possible to create a unified view of enterprise data.
Useful links
We’ve discussed a lot in this guide, but there might still be more you want to discover about data fabric. Browse these handy sources to learn more.