What is a Knowledge Graph and How Does it Work?
Your essential guide to knowledge graph: what it is, how does it work, benefits, use cases and challenges. Learn how you can structure a knowledge graph and leverage knowledge graph technology to understand and use context.
What is a knowledge graph?
A knowledge graph represents information about data and entities, such as people, businesses, places, concepts, events, and objects, and the relationships between them. These insights are shown in the form of graphs, hence the name ‘knowledge graphs’.
Knowledge graphs allow users to access relevant information and find connections they weren’t aware of. They can be updated as information and context evolves, offering more flexibility than more rigid data solutions. Each company will have their own version with their own data.
What are the three areas of a knowledge graph?
The three parts of a knowledge graph are:
Nodes
Entities that can be physical (an object, place or person) or an abstract concept, represented by the graph.
Edges
The links between the nodes and the relevant context.
Attributes
Additional information about each entity.
Together, these three components form a structured and interconnected dataset that enhances the understanding and usability of complex information.
How does a knowledge graph work?
A knowledge graph works by organizing and linking data points (entities) through relationships, extracting the information about those entities and their relationships from the data itself.
The information provided in a knowledge graph is usually sourced from multiple datasets. Data that comes from various sources may be structured differently, so it needs to be standardized, processed and unified to be used in a graph. The step often involves entity resolution — the process of identifying the records that reference the same real-world objects.
Some knowledge graphs have an additional semantic layer with descriptions called ontologies, which explain exactly what the entities are and the relationships between them.
How do you structure a knowledge graph?
A knowledge graph shows how data points are interconnected, highlighting the relationships between them. The following steps are typically involved in creation of a knowledge graph:
- 1. Defining the entities or nodes, which represent the main concepts or items in your data set
- 2. Establishing relationships or edges between these entities to illustrate how they are connected
- 3. Applying schema or ontology to maintain uniformity across the graph
- 4. Enriching the graph with properties and attributes that provide more context and details about each entity and relationship
- 5. Validating the knowledge graph through iterative testing and refinement to ensure it meets your analytical or operational needs
This structured approach not only enhances data integration but also improves insights and decision-making capabilities.
What are knowledge graphs used for?
The flexibility of knowledge graphs means they can be used in multiple ways across a variety of industries:
Finance
Knowledge graphs are used for preventing crimes (for example in protective initiatives like know your customer (KYC) and anti-money laundering and for investigating them.
Retail
Information the purchase behavior of individuals and demographic groups can be used to plan strategies for upselling or cross selling.
Healthcare
Relationships in medical research are categorized, helping with diagnoses and treatment.
Search
Google uses their knowledge graph to produce information in the search engine results pages (SERPs).
Entertainment
Information about user engagement is used to make content recommendations.
What is the difference between a graph database and a knowledge graph?
A graph database and a knowledge graph are conceptually different things although both are relevant for the conversation about graph analytics.
A graph database is a platform that is designed to represent and store data in graph structures, focusing on the relationships between different data points. It uses nodes, edges, and properties to build a flexible data model that is efficient for traversing complex connections.
While a knowledge graph itself is a data model that represents the information as nodes, edges and their related attributes. Analytical tools that work with a knowledge graph go beyond storing data, enabling more sophisticated queries and insights.
How does a knowledge graph use machine learning?
Machine learning algorithms are applied on knowledge graphs to analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, relationships, and concepts. These insights are then used to enrich the view of the entities.
What is a knowledge graph in gen AI?
Generative artificial intelligence, also known as gen AI, refers to algorithms used to create content. Knowledge graphs provide a foundation for gen AI by representing how various entities are linked, so the algorithm can retrieve this information and use it for the content creation process in a more accurate and contextually relevant manner. This advanced form of information retrieval not only accelerates the search process but also significantly improves the quality of insights derived from complex datasets.
Knowledge graph FAQs
Is a knowledge graph a data model?
Yes. A knowledge graph is a type of data model showing how the nodes, edges and labels are interlinked, providing context for the data. It’s different from a traditional data model, in that it highlights these connections instead of focusing on data efficiency and storage.
Is a knowledge graph a neural network?
No. Knowledge graphs and neural networks are both graphs, but they’re structured differently and used in relation to one another.
A knowledge graph represents information, while a neural network is a machine learning model. It identifies the significance of the nodes and edges in a knowledge graph and uses this information to compare options and come to conclusions.
A neural network is a computational model inspired by the human brain, consisting of interconnected nodes or neurons that process data and learn patterns through training.
While both serve the purpose of enhancing machine learning and AI capabilities, they operate on fundamentally different principles and are used for distinct applications.
Is a knowledge graph part of NLP?
NLP, or natural language processing, is a field of AI “that uses machine learning to enable computers to understand and communicate with human language”, according to IBM. Knowledge graphs use NLP in a process called semantic enrichment, which creates an overview of the data before ingestion. This means the objects and the relationships between them can be understood when the data is ingested, and the information can be used in the most beneficial way. It can also be compared to existing data.
Created knowledge graphs could also be used as part of RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) for LLMs (Large Language Models) to optimize the output of the latter and ground the model with available contextual information.
What is ontology in a knowledge graph?
As we’ve touched on above, some knowledge graphs have an additional semantic layer with descriptions — these are called ontologies. Ontologies explain what the entities are and define the relationships between them, providing a common vocabulary to ensure data from various sources can be linked and understood. By establishing these semantic relationships, ontology enhances the ability to integrate disparate data silos, making it easier to query and extract meaningful insights.
What is the difference between a knowledge graph and semantic layer?
A knowledge graph provides context by representing information about data and entities, such as concepts, events, objects and situations, and the relationships between them.
A semantic layer simplifies complex data so users can gain insights without needing deep technical expertise.
What is the difference between semantic search and a knowledge graph? 
Semantic search is a search engine technology. It deciphers the literal meaning of a search query, the searcher’s intent, and the context in which their search sits in order to provide results which reflect what the user was asking about.
For example, if the searcher were to type in “decision intelligence platform”, semantic search would understand they were looking for a commercial tool and provide relevant results.
In contrast, a knowledge graph is a representation of data that can itself be searched.
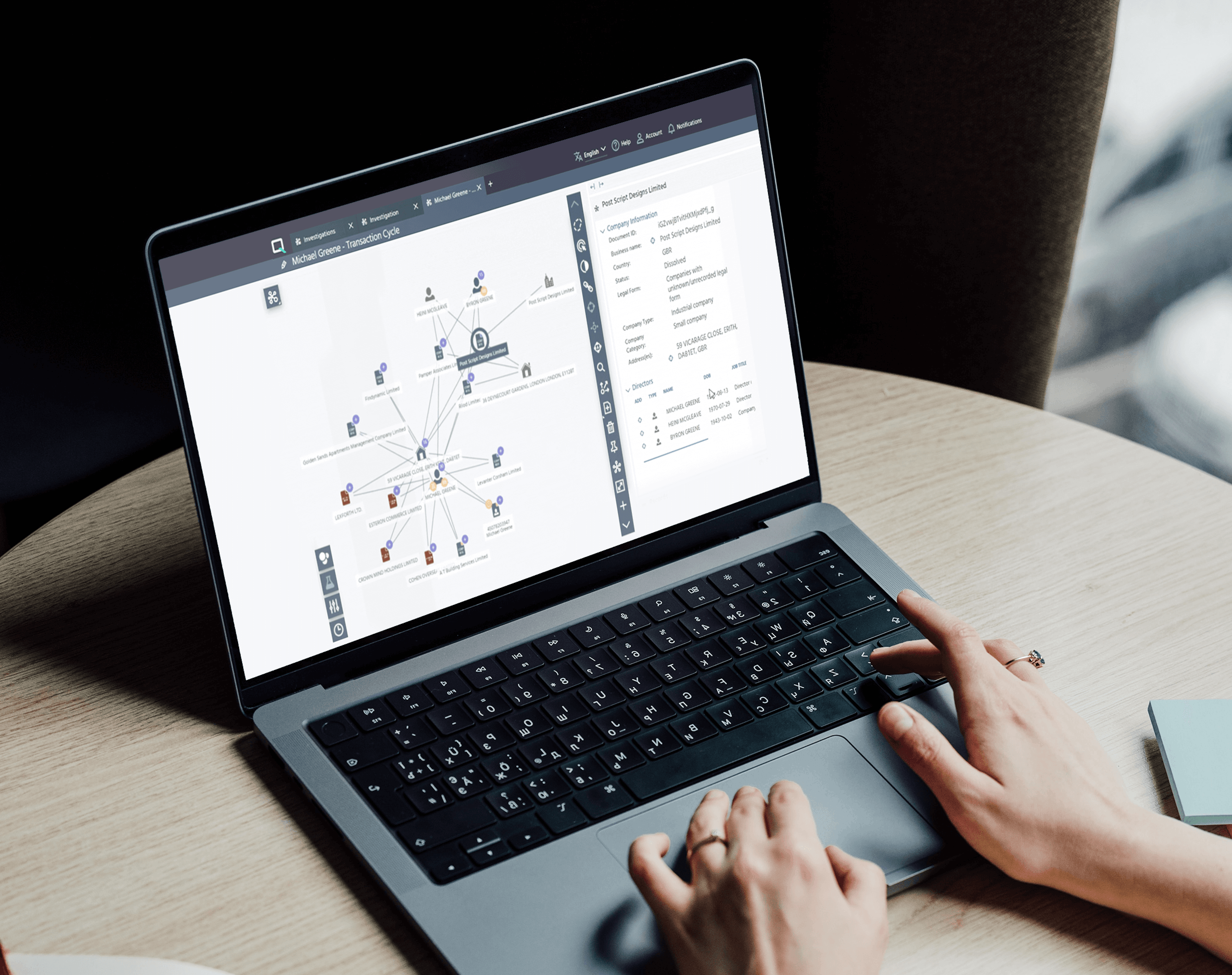
Quantexa’s knowledge graph technology equips data scientists with the tools to understand and use context represented in graphs in the models they build and analysis they conduct. This technology is a part of our Decision Intelligence Platform, and the insights and outputs of graph analytics are productionalized to power business and operational decisions. It brings together billions of data points from internal and external data sources to create dynamic views of the entities, connections, and relationships that matter to your organization, and uncovers insights relevant for your use case.
Useful links
We’ve discussed a lot in this guide, but there might still be more you want to discover about knowledge graph. Browse these handy sources to learn more.